Data Design Project Overview
Don't be afraid of being wrong.
Matt David, Cohort 18
Example
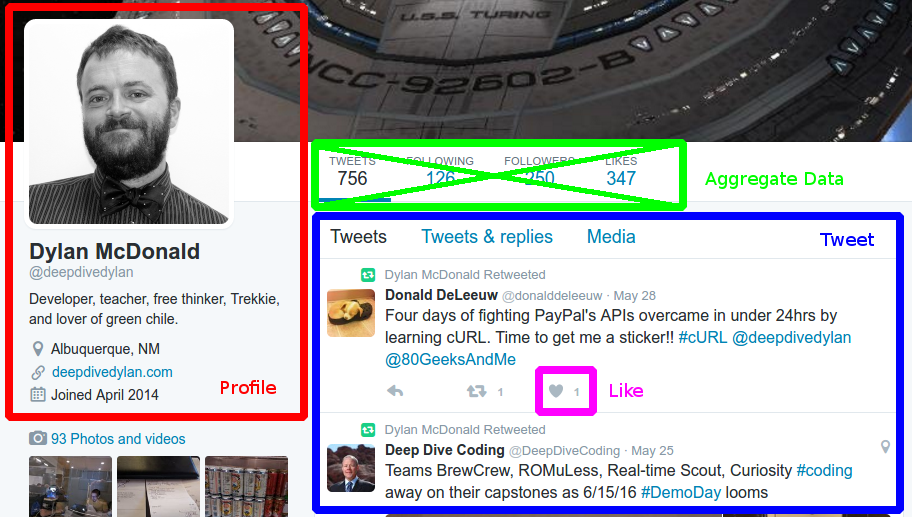
Figure 1: Visual Representation of the Data Design Process
Entities & Attributes
Conceptual Model
Profile
- profileId (primary key)
- profileActivationToken (for account verification)
- profileAtHandle
- profileEmail
- profileHash (for account password)
- profilePhone
Tweet
- tweetId (primary key)
- tweetProfileId (foreign key)
- tweetContent
- tweetDate
Like
- likeProfileId (foreign key)
- likeTweetId (foreign key)
- likeDate
Relations
- One Profile can write many Tweets - (1 to many)
- Many Tweets can be liked by many Profiles - (many to many)
Example ERD
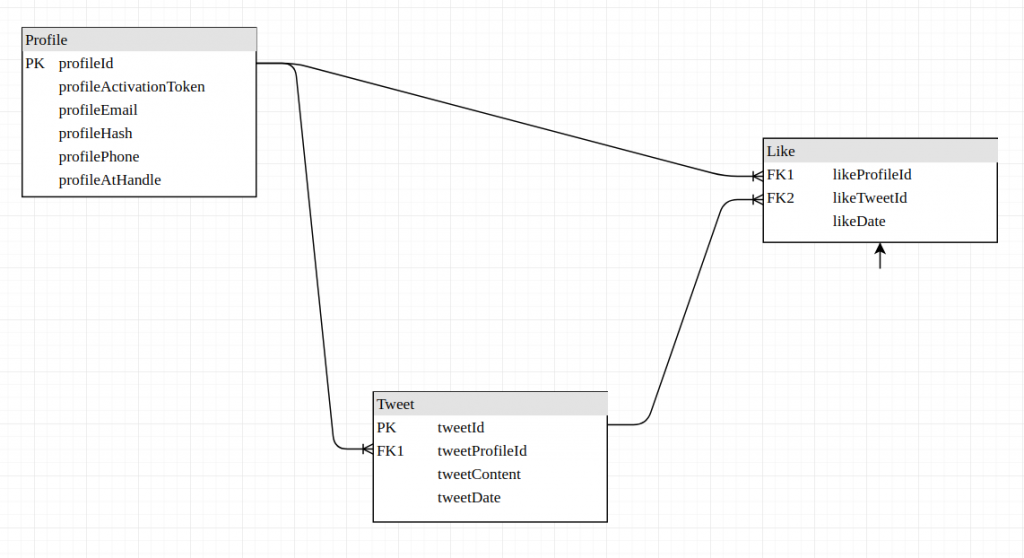
Figure 2: Example ERD for the Twitter SQL Database
Example Data Design Layer (DDL)
-- The statement below sets the collation of the database to utf8 ALTER DATABASE your_database_name_CHANGE_ME CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci; -- this is a comment in SQL (yes, the space is needed!) -- these statements will drop the tables and re-add them -- this is akin to reformatting and reinstalling Windows (OS X never needs a reinstall...) ;) -- never ever ever ever ever ever ever ever ever ever ever ever ever ever ever ever ever ever ever ever -- do this on live data!!!! DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `like`; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS tweet; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS profile; -- the CREATE TABLE function is a function that takes tons of arguments to layout the table's schema CREATE TABLE profile ( -- this creates the attribute for the primary key -- not null means the attribute is required! profileId BINARY(16) NOT NULL, profileActivationToken CHAR(32), profileAtHandle VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL, profileEmail VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL, -- to make something optional, exclude the not null profileHash CHAR(97) NOT NULL, profilePhone VARCHAR(32), -- to make sure duplicate data cannot exist, create a unique index UNIQUE(profileAtHandle), UNIQUE(profileEmail), -- this officiates the primary key for the entity PRIMARY KEY(profileId) ); -- create the tweet entity CREATE TABLE tweet ( -- this is for yet another primary key... tweetId BINARY(16) NOT NULL, -- this is for a foreign key tweetProfileId BINARY(16) NOT NULL, tweetContent VARCHAR(140) NOT NULL, tweetDate DATETIME(6) NOT NULL, -- this creates an index before making a foreign key INDEX(tweetProfileId), -- this creates the actual foreign key relation FOREIGN KEY(tweetProfileId) REFERENCES profile(profileId), -- and finally create the primary key PRIMARY KEY(tweetId) ); -- create the like entity (a weak entity from an m-to-n for profile --> tweet) CREATE TABLE `like` ( -- these are still foreign keys likeProfileId BINARY(16) NOT NULL, likeTweetId BINARY(16) NOT NULL, likeDate DATETIME(6) NOT NULL, -- index the foreign keys INDEX(likeProfileId), INDEX(likeTweetId), -- create the foreign key relations FOREIGN KEY(likeProfileId) REFERENCES profile(profileId), FOREIGN KEY(likeTweetId) REFERENCES tweet(tweetId), -- finally, create a composite foreign key with the two foreign keys PRIMARY KEY(likeProfileId, likeTweetId) );